PCNA Antibody [Knockout Validated]
Purified Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (Mab)
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS: 1
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, FC, IHC-P, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P12004 |
| Other Accession | P61258 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Mouse |
| Clonality | monoclonal |
| Isotype | IgG1,k |
| Clone/Animal Names | 1655CT506.10.26 |
| Calculated MW | 28769 Da |
| Gene ID | 5111 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Proliferating cell nuclear antigen, PCNA, Cyclin, PCNA |
| Target/Specificity | This PCNA antibody is generated from a mouse immunized with a recombinant protein of human PCNA. |
| Dilution | WB~~1:2000 FC~~1:25 IHC-P~~1:25 E~~Use at an assay dependent concentration. |
| Format | Purified monoclonal antibody supplied in PBS with 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide. This antibody is purified through a protein G column, followed by dialysis against PBS. |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 2 weeks. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | PCNA Antibody [Knockout Validated] is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | PCNA |
|---|---|
| Function | Auxiliary protein of DNA polymerase delta and epsilon, is involved in the control of eukaryotic DNA replication by increasing the polymerase's processibility during elongation of the leading strand (PubMed:35585232). Induces a robust stimulatory effect on the 3'-5' exonuclease and 3'-phosphodiesterase, but not apurinic-apyrimidinic (AP) endonuclease, APEX2 activities. Has to be loaded onto DNA in order to be able to stimulate APEX2. Plays a key role in DNA damage response (DDR) by being conveniently positioned at the replication fork to coordinate DNA replication with DNA repair and DNA damage tolerance pathways (PubMed:24939902). Acts as a loading platform to recruit DDR proteins that allow completion of DNA replication after DNA damage and promote postreplication repair: Monoubiquitinated PCNA leads to recruitment of translesion (TLS) polymerases, while 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitination of PCNA is involved in error-free pathway and employs recombination mechanisms to synthesize across the lesion (PubMed:24695737). |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus. Note=Colocalizes with CREBBP, EP300 and POLD1 to sites of DNA damage (PubMed:24939902). Forms nuclear foci representing sites of ongoing DNA replication and vary in morphology and number during S phase (PubMed:15543136). Co-localizes with SMARCA5/SNF2H and BAZ1B/WSTF at replication foci during S phase (PubMed:15543136). Together with APEX2, is redistributed in discrete nuclear foci in presence of oxidative DNA damaging agents |
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Auxiliary protein of DNA polymerase delta and is involved in the control of eukaryotic DNA replication by increasing the polymerase's processibility during elongation of the leading strand. Induces a robust stimulatory effect on the 3'- 5' exonuclease and 3'-phosphodiesterase, but not apurinic- apyrimidinic (AP) endonuclease, APEX2 activities. Has to be loaded onto DNA in order to be able to stimulate APEX2. Plays a key role in DNA damage response (DDR) by being conveniently positioned at the replication fork to coordinate DNA replication with DNA repair and DNA damage tolerance pathways. Acts as a loading platform to recruit DDR proteins that allow completion of DNA replication after DNA damage and promote postreplication repair: Monoubiquitinated PCNA leads to recruitment of translesion (TLS) polymerases, while 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitination of PCNA is involved in error-free pathway and employs recombination mechanisms to synthesize across the lesion.
References
Almendral J.M.,et al.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84:1575-1579(1987).
Travali S.,et al.J. Biol. Chem. 264:7466-7472(1989).
Ota T.,et al.Nat. Genet. 36:40-45(2004).
Deloukas P.,et al.Nature 414:865-871(2001).
Mural R.J.,et al.Submitted (SEP-2005) to the EMBL/GenBank/DDBJ databases.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.





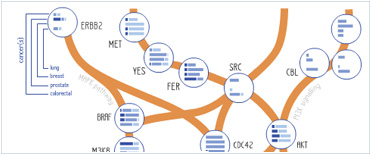







 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
![WB - PCNA Antibody [Knockout Validated] AM8545b](/assets/uploads/products/202404/AM8545b_WB_2.jpg)
![WB - PCNA Antibody [Knockout Validated] AM8545b](/assets/uploads/products/201601/AM8545b_WB_1.jpg)
![IHC - PCNA Antibody [Knockout Validated] AM8545b](/assets/uploads/products/201601/AM8545b_ihc_20200903.png)
![IHC-P - PCNA Antibody [Knockout Validated] AM8545b](/assets/uploads/products/201605/AM8545b_IHC_1.jpg)
![FC - PCNA Antibody [Knockout Validated] AM8545b](/assets/uploads/products/201605/AM8545b_FC_1.jpg)
